Discovering a water heater leaking from the top hot water outlet is a homeowner’s nightmare, often signaling a potentially costly and disruptive problem. This specific type of leak, however, presents unique diagnostic challenges compared to more common leaks around the base of the tank. The source of the leak might not be immediately obvious, requiring a systematic approach to identify the underlying cause and implement the correct repair. We will delve into the possible culprits behind a water heater leaking from the top hot water outlet, providing a step-by-step guide to troubleshooting and resolution; Understanding the intricacies of your water heater’s design and operation is key to effectively tackling this problem.
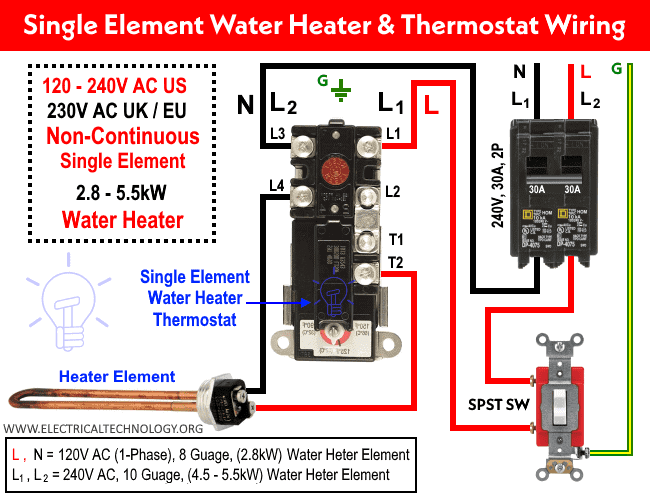
Understanding the Anatomy and Potential Leak Points
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s crucial to understand the components near the top hot water outlet. Key elements include:
- Hot Water Outlet Pipe: This pipe carries heated water from the tank to your plumbing system.
- Dielectric Nipple (if present): Often installed to prevent galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals (e.g., copper pipe and a steel tank).
- Pressure Relief Valve (PRV): Designed to release excess pressure within the tank. While not directly part of the hot water outlet, a malfunctioning PRV can sometimes cause water to accumulate near the top of the tank, mimicking a leak from the outlet.
- Tank Top: The welded seam or fitted top of the water heater itself.
Troubleshooting Steps for a Top Outlet Leak
- Safety First: Turn off the power (for electric heaters) or gas supply (for gas heaters) to the water heater. Then, turn off the water supply to the heater.
- Inspect the Hot Water Outlet Pipe Connection: Check the connection point between the hot water outlet pipe and the tank. Look for signs of corrosion, loose fittings, or damaged threads. Try tightening the connection (if possible) with a pipe wrench, but be careful not to overtighten and strip the threads.
- Examine the Dielectric Nipple: If a dielectric nipple is present, inspect it for cracks, corrosion, or leaks. These nipples are prone to failure over time. Replacement is often the best solution if any damage is found.
- Check the Pressure Relief Valve (PRV): Operate the PRV manually by lifting the lever. If it continues to drip or leak after releasing the lever, the valve is likely faulty and needs to be replaced. Water accumulating around the top of the tank, even if the leak appears to be from the outlet, could be originating from a leaking PRV.
- Inspect the Tank Top: Carefully examine the tank top around the hot water outlet for any signs of rust, corrosion, or cracks. A leak originating from the tank itself indicates a serious problem, and replacement of the entire water heater is usually necessary.
Repair Options and When to Call a Professional
Depending on the source of the leak, repair options vary:
- Loose Connection: Tightening the fitting may resolve the issue.
- Damaged Dielectric Nipple: Replace the nipple.
- Faulty PRV: Replace the PRV.
- Tank Leak: Replacement of the entire water heater is recommended.
For complex repairs, especially those involving gas lines or electrical connections, it is always best to consult a qualified plumber. Attempting repairs without the proper knowledge and tools can be dangerous. The presence of a water heater leaking from the top hot water outlet can be frustrating, but by following these steps, you can diagnose the problem effectively and determine the best course of action. In the end, addressing this issue promptly is essential to prevent further damage and ensure the safety of your home.
PREVENTATIVE MEASURES AND MAINTENANCE
Proactive maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of your water heater and minimize the likelihood of encountering problems like leaks. Regular inspections and a few simple preventative measures can save you time, money, and the inconvenience of unexpected breakdowns.
ANNUAL INSPECTION CHECKLIST:
– Check for Corrosion: Visually inspect the tank, pipes, and fittings for any signs of rust or corrosion. Address any minor surface rust promptly with a wire brush and rust-inhibiting paint.
– Test the Pressure Relief Valve (PRV): Manually operate the PRV at least once a year to ensure it’s functioning correctly. If it sticks or doesn’t reseat properly, replace it.
– Flush the Tank: Sediment buildup inside the tank can reduce efficiency and contribute to premature failure. Flush the tank annually to remove sediment. This typically involves connecting a hose to the drain valve at the bottom of the tank and running water until it runs clear.
– Inspect Anode Rod (if accessible): The anode rod is a sacrificial metal rod designed to corrode instead of the tank itself. If the rod is significantly corroded, it should be replaced. Some water heaters have an accessible anode rod for easy inspection and replacement.
WATER QUALITY CONSIDERATIONS
The quality of your water can have a significant impact on the lifespan of your water heater. Hard water, which is high in mineral content, can accelerate scale buildup inside the tank, reducing efficiency and potentially leading to leaks. If you have hard water, consider installing a water softener to protect your plumbing and appliances.
LONG-TERM SOLUTIONS AND UPGRADES
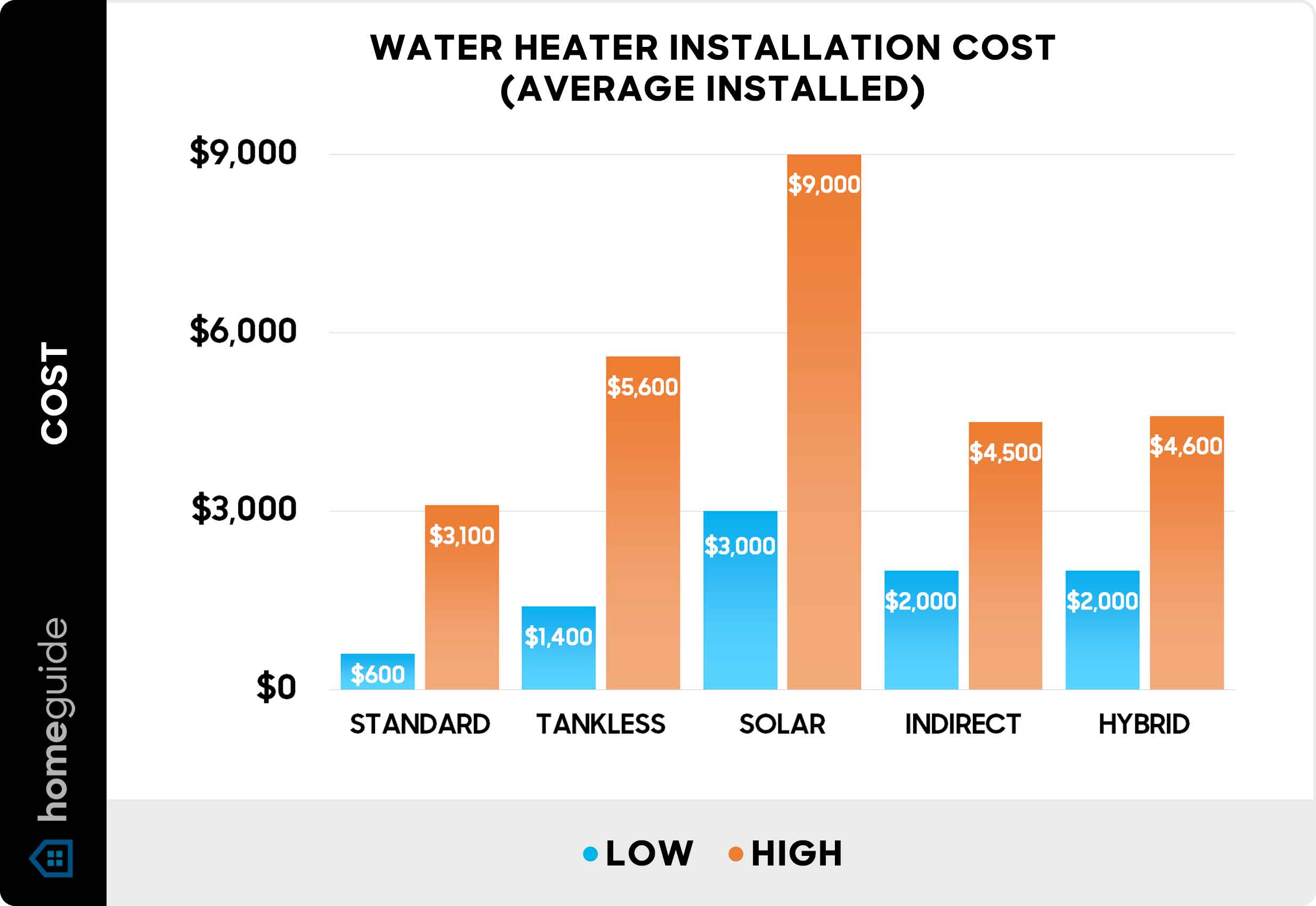
If your water heater is old or has required frequent repairs, it might be time to consider a replacement. Newer models are often more energy-efficient, which can save you money on your utility bills. Tankless water heaters, for example, provide hot water on demand and eliminate the need for a storage tank, reducing standby heat loss. Other considerations include:
– Tank Size: Choose a tank size that meets your household’s hot water needs. An undersized tank will lead to frequent hot water shortages, while an oversized tank will waste energy.
– Energy Efficiency: Look for models with high energy factor (EF) ratings. The higher the EF rating, the more efficient the water heater.
– Warranty: Consider the warranty offered by the manufacturer. A longer warranty provides peace of mind and protection against defects.