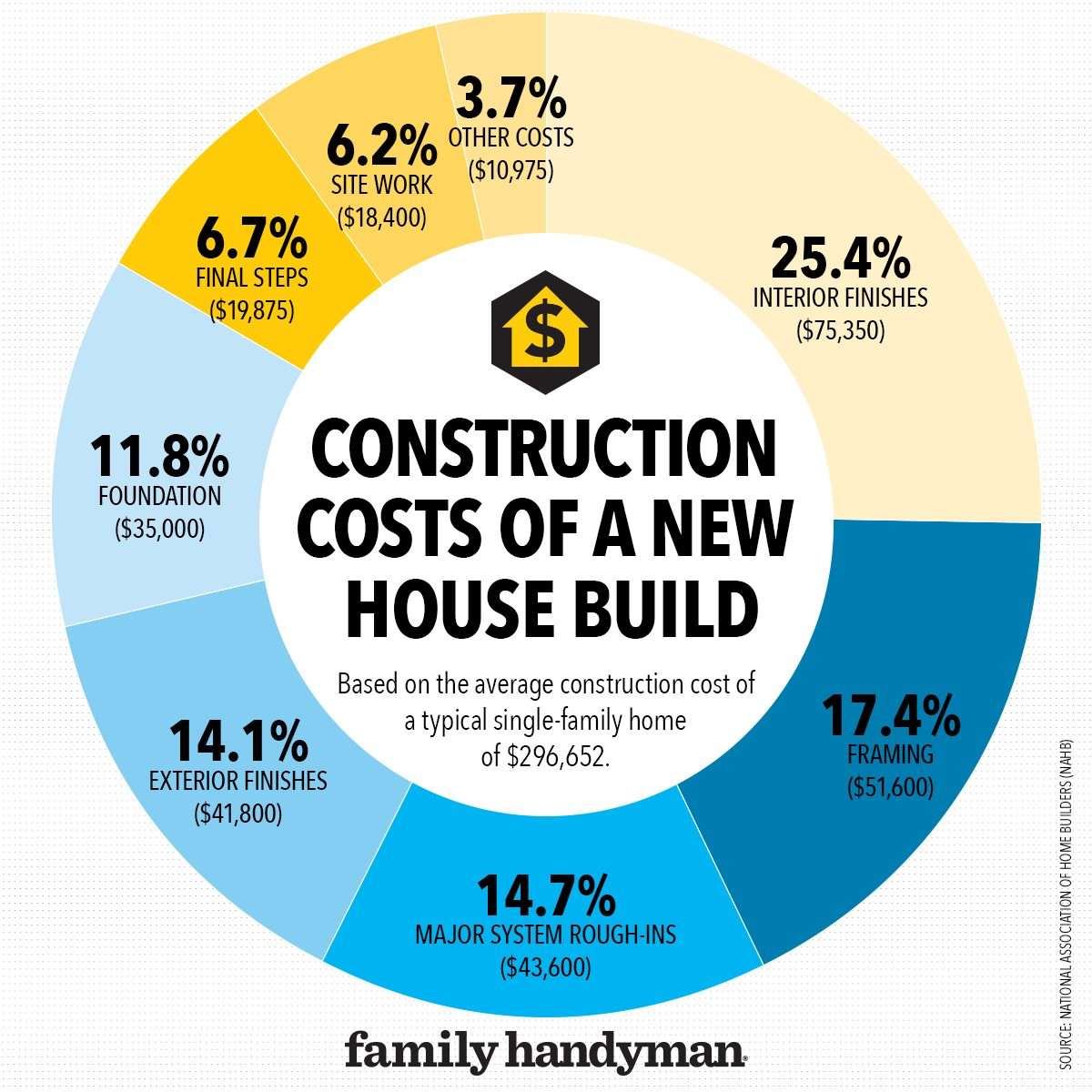
The world of construction is constantly evolving‚ but a growing trend is looking back to the past for inspiration and resources: architectural salvage. Using architectural salvage reclaimed building materials offers a unique opportunity to blend historical charm with modern design principles. This practice not only reduces waste and minimizes environmental impact‚ but also allows for the creation of spaces imbued with character and a sense of history. Embracing architectural salvage reclaimed building materials is a conscious choice that supports sustainable practices and results in truly one-of-a-kind projects. By thoughtfully incorporating these elements‚ architects and designers can create spaces that tell a story and resonate with authenticity.
The Allure of Reclaimed Materials
There’s an undeniable appeal to reclaimed building materials. They carry with them the patina of age‚ the marks of previous lives‚ and a richness that simply cannot be replicated with new construction materials. This inherent character transforms spaces‚ adding depth‚ warmth‚ and a connection to the past. Imagine reclaimed hardwood floors creaking softly underfoot‚ or a vintage door serving as a stunning focal point. These elements are not just building blocks; they are conversation starters‚ pieces of art that contribute to the overall ambiance of a home or commercial space.
Benefits Beyond Aesthetics
- Environmental Sustainability: Reusing materials significantly reduces landfill waste and the demand for new resources.
- Unique Character: Adds historical charm and individuality to any project.
- Cost Savings (Potentially): While not always cheaper upfront‚ reclaimed materials can be more durable and require less maintenance.
- Support for Local Economies: Many architectural salvage businesses are small‚ local enterprises.
Finding and Using Architectural Salvage
Sourcing architectural salvage can be an adventure in itself. Antique shops‚ demolition sites‚ architectural salvage yards‚ and online marketplaces are all potential treasure troves. The key is to be patient‚ persistent‚ and to have a clear vision for how you intend to incorporate the materials into your project. Remember to thoroughly inspect any reclaimed item for structural integrity‚ pests‚ and lead paint (especially in older materials).
Tips for Successful Integration
- Plan Ahead: Determine the specific materials you need and how they will fit into your design.
- Thorough Inspection: Check for damage‚ pests‚ and hazardous materials.
- Proper Cleaning and Restoration: Bring reclaimed items back to their former glory while preserving their character.
- Professional Installation: Ensure proper installation to maintain structural integrity and safety.
Architectural Salvage: A Comparative Look
| Feature | Reclaimed Materials | New Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Low | High |
| Character & Uniqueness | High | Low |
| Cost | Variable (can be lower) | Generally Predictable |
| Availability | Limited & Variable | Readily Available |
Ultimately‚ the decision to incorporate architectural salvage into a project depends on a variety of factors‚ including budget‚ design preferences‚ and commitment to sustainability. As we move towards a more eco-conscious future‚ the practice of utilizing architectural salvage reclaimed building materials will undoubtedly continue to grow in popularity‚ offering a unique and rewarding way to create beautiful‚ sustainable‚ and historically rich spaces. By embracing the past‚ we can build a better future‚ one reclaimed brick at a time.
The integration of reclaimed materials transcends mere aesthetic considerations; it embodies a commitment to responsible resource management and the preservation of historical narratives. The conscious selection of architectural salvage allows designers and builders to mitigate the environmental impact associated with resource extraction and manufacturing processes inherent in the production of new building components. Furthermore‚ it contributes to the conservation of cultural heritage by repurposing elements that might otherwise be relegated to demolition and oblivion.
ADDRESSING POTENTIAL CHALLENGES AND CONSIDERATIONS
While the incorporation of reclaimed materials presents numerous advantages‚ certain challenges must be addressed to ensure a successful and structurally sound outcome. The variability in material condition‚ availability‚ and conformity to contemporary building codes necessitates meticulous planning and execution. A thorough assessment of the structural integrity of reclaimed elements is paramount‚ often requiring the expertise of qualified engineers and building inspectors. Moreover‚ careful consideration must be given to the compatibility of reclaimed materials with modern construction techniques and systems. This may involve modifications‚ adaptations‚ and the implementation of specialized installation methods to ensure seamless integration and long-term performance.
NAVIGATING REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS AND SAFETY STANDARDS
The utilization of architectural salvage must adhere to all applicable regulatory requirements and safety standards. This includes compliance with building codes pertaining to structural stability‚ fire resistance‚ and the presence of hazardous materials such as lead paint and asbestos. Prior to incorporation‚ reclaimed materials should undergo rigorous testing and remediation processes to ensure they meet or exceed the standards required for safe and legal use. Collaboration with local building officials and code enforcement agencies is crucial to obtain the necessary permits and approvals. Adherence to these protocols ensures the safety of occupants and the long-term viability of the structure.
THE FUTURE OF ARCHITECTURAL SALVAGE IN SUSTAINABLE CONSTRUCTION
The future of architectural salvage is inextricably linked to the growing emphasis on sustainable construction practices and the circular economy. As awareness of the environmental consequences of resource depletion and waste generation intensifies‚ the demand for reclaimed materials is poised to increase exponentially. Technological advancements in material processing‚ restoration techniques‚ and digital inventory management will further facilitate the integration of architectural salvage into mainstream construction projects. The development of standardized grading systems and certification programs will enhance transparency and confidence in the quality and provenance of reclaimed materials. Furthermore‚ the integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology will enable architects and engineers to seamlessly incorporate reclaimed elements into digital models‚ optimizing design and construction processes.
In conclusion‚ the responsible and innovative utilization of architectural salvage represents a paradigm shift in the construction industry. It underscores a commitment to environmental stewardship‚ the preservation of cultural heritage‚ and the creation of spaces that are both aesthetically compelling and functionally superior. As the principles of sustainability gain further traction‚ the integration of reclaimed building materials will become an increasingly integral component of responsible design and construction practices. The adoption of architectural salvage transcends mere trendiness; it signifies a conscious decision to build a more sustainable and historically resonant future.