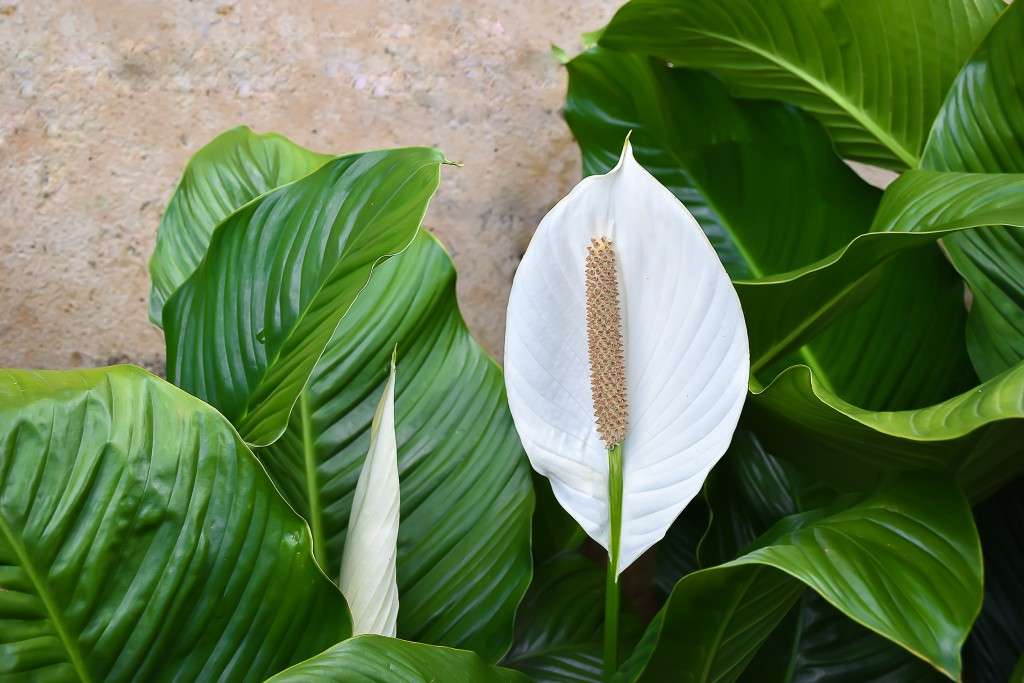
Imagine a touch of tranquility gracing your living space‚ a vibrant splash of nature brought indoors. This is the allure of an indoor plant with white flowers and green leaves. Beyond its aesthetic appeal‚ such a plant offers a myriad of benefits‚ purifying the air and fostering a sense of calm. Discover the captivating beauty and enduring charm of an indoor plant with white flowers and green leaves‚ a living testament to nature’s artistry that elevates any interior setting. The gentle contrast of pristine white blossoms against verdant foliage creates a captivating visual harmony‚ a serene escape from the everyday hustle.
Unveiling the Lunar Emerald: A Hypothetical Specimen
Let’s delve into the characteristics of a hypothetical‚ yet enchanting‚ indoor plant‚ which we’ll affectionately call the “Lunar Emerald.” This plant is imagined to possess striking white flowers and lush green leaves‚ embodying elegance and vitality. While not a real species (yet!)‚ it serves as a perfect example for exploring the care and beauty of such botanical wonders.
Leaf Morphology and Floral Structure
* **Leaves:** Deep emerald green‚ glossy‚ and broadly ovate‚ providing a rich backdrop for the flowers. They exhibit a slight undulation along the edges‚ adding a touch of whimsy.
* **Flowers:** Pure white‚ star-shaped blossoms that emerge in clusters. Each flower boasts delicate petals with a subtle‚ almost translucent quality‚ reminiscent of moonlight.
* **Growth Habit:** Upright and bushy‚ reaching a moderate height of approximately 2-3 feet‚ making it ideal for indoor cultivation.
Caring for Your Lunar Emerald (or Similar Indoor Plant)
Maintaining the health and beauty of your indoor plant with white flowers and green leaves requires attention to a few key elements:
* **Light:** Bright‚ indirect sunlight is crucial. Avoid harsh‚ direct sunlight‚ which can scorch the leaves.
* **Watering:** Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry. Ensure proper drainage to prevent root rot.
* **Humidity:** Prefers moderate to high humidity. Consider using a humidifier or placing the plant on a pebble tray filled with water.
* **Temperature:** Maintain a consistent temperature between 65-75°F (18-24°C).
* **Fertilizer:** Feed with a balanced liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Comparative Analysis: Lunar Emerald vs. Peace Lily
| Feature | Lunar Emerald (Hypothetical) | Peace Lily (Spathiphyllum) |
|---|---|---|
| Leaf Shape | Broadly ovate‚ slightly undulating | Lance-shaped‚ smooth |
| Flower Shape | Star-shaped | Spadix and spathe (hooded flower) |
| Light Requirements | Bright‚ indirect light | Low to moderate light |
| Humidity Requirements | Moderate to high | High |
The enduring appeal of the indoor plant with white flowers and green leaves lies in its ability to transform any space into a tranquil sanctuary‚ a testament to the calming power of nature. By understanding its needs and providing proper care‚ you can enjoy the serene beauty of this botanical treasure for years to come.
Here’s a continuation of the text‚ maintaining a neutral style and incorporating HTML tags:
TROUBLESHOOTING COMMON ISSUES
Even with diligent care‚ your Lunar Emerald (or similar plant) might encounter some common issues. Early detection and appropriate action can prevent these problems from escalating.
– Yellowing Leaves: Often caused by overwatering‚ underwatering‚ or insufficient light. Assess the soil moisture and light conditions and adjust accordingly. Consider repotting if the soil is heavily compacted.
– Brown Leaf Tips: Usually indicates low humidity or fluoride toxicity from tap water. Increase humidity levels and use filtered or distilled water for watering.
– Pests (e.g.‚ mealybugs‚ spider mites): Inspect the plant regularly for signs of infestation. Isolate the affected plant and treat with insecticidal soap or neem oil‚ following product instructions carefully.
– Lack of Flowering: May be due to insufficient light or inadequate fertilization. Move the plant to a brighter location and ensure it receives a balanced fertilizer during the growing season.
PROPAGATION TECHNIQUES
Expanding your collection of Lunar Emeralds (or similar plants) can be achieved through various propagation methods. These techniques allow you to create new plants from existing ones‚ fostering a thriving indoor garden.
STEM CUTTINGS
1. Select a healthy stem with several leaves.
2. Cut the stem just below a node (where a leaf emerges).
3. Remove the lower leaves‚ leaving only a few at the top.
4. Place the cutting in water or directly into a well-draining potting mix.
5. If using water‚ change it every few days. Roots should develop within a few weeks.
6. Once roots are established‚ transplant the cutting into a pot with suitable potting mix.
DIVISION
This method is applicable if your plant has multiple stems growing from the base.
1. Gently remove the plant from its pot.
2. Carefully separate the stems‚ ensuring each division has its own roots.
3. Repot each division into its own pot with fresh potting mix.
THE PSYCHOLOGICAL BENEFITS OF INDOOR PLANTS
Beyond their aesthetic appeal‚ indoor plants‚ including those with white flowers and green leaves‚ offer a range of psychological benefits. Studies have shown that plants can reduce stress levels‚ improve mood‚ and enhance cognitive function. The simple act of caring for a plant can be a therapeutic and rewarding experience‚ fostering a sense of connection to nature and promoting overall well-being. Consider the Lunar Emerald as more than just a decorative element‚ but as a source of tranquility and vitality within your living space.