The allure of energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprint has propelled the heat pump water heater installation requirements to the forefront of modern home improvement. However‚ simply purchasing a unit isn’t enough; proper installation is crucial for realizing the promised benefits and ensuring long-term performance. Navigating the intricacies of heat pump water heater installation requirements can feel overwhelming‚ but understanding the key considerations will empower you to make informed decisions and guarantee a safe and effective setup. From ventilation needs to electrical specifications‚ a meticulous approach is paramount to maximizing efficiency and longevity.
Understanding Key Installation Factors
Installing a heat pump water heater differs significantly from traditional electric or gas models. These differences stem from the heat pump’s reliance on ambient air to extract heat‚ impacting ventilation needs‚ placement considerations‚ and condensate management.
Ventilation and Airflow
Unlike conventional water heaters that generate heat internally‚ heat pump water heaters draw heat from the surrounding air. This means adequate ventilation is absolutely critical. Insufficient airflow can significantly reduce the unit’s efficiency and even lead to premature failure. Consider these points:
- Minimum Room Size: Most manufacturers specify a minimum room size to ensure sufficient air volume. A general guideline is at least 1‚000 cubic feet‚ but always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for specific requirements.
- Air Circulation: Ensure the room is not sealed off. The heat pump needs access to a consistent supply of fresh air. Consider providing ventilation through vents or by leaving a door slightly ajar.
- Avoid Confined Spaces: Avoid installing the unit in small‚ enclosed closets or areas with limited airflow.
Location Considerations
Choosing the right location is another vital aspect of a successful heat pump water heater installation. Several factors should be considered:
- Ambient Temperature: Heat pumps perform optimally in warmer environments. Avoid installing them in unheated areas where temperatures frequently drop below 40°F (4°C).
- Proximity to Living Areas: While heat pumps are relatively quiet‚ they do generate some noise. Consider the proximity to bedrooms or other sensitive living areas when selecting a location.
- Drainage: Heat pumps produce condensate‚ so the installation location must have access to a suitable drain.
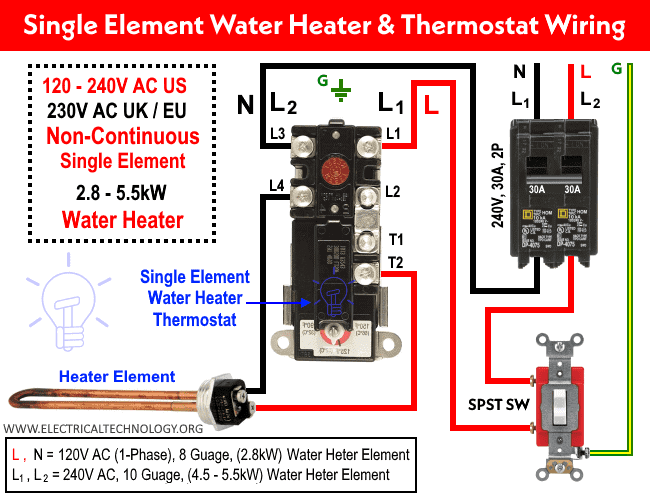
Electrical and Plumbing Requirements
Beyond ventilation and location‚ the electrical and plumbing connections must adhere to specific codes and guidelines.
Electrical Specifications
Heat pump water heaters typically require a dedicated 240-volt circuit. Consult a qualified electrician to ensure your home’s electrical system can accommodate the new load. Furthermore:
- Dedicated Circuit: Do not share the circuit with other appliances.
- Correct Breaker Size: Use the correct breaker size as specified by the manufacturer.
- Proper Grounding: Ensure the unit is properly grounded to prevent electrical hazards.
Plumbing Connections
The plumbing connections for a heat pump water heater are similar to those for a conventional water heater‚ but it’s crucial to use the correct materials and techniques:
- Compatible Piping: Use piping materials that are compatible with potable water and can withstand the temperatures involved.
- Pressure Relief Valve: Install a properly functioning pressure relief valve to prevent over-pressurization.
- Drainage System: Connect the condensate drain to a suitable drainage system‚ ensuring proper slope and avoiding obstructions.
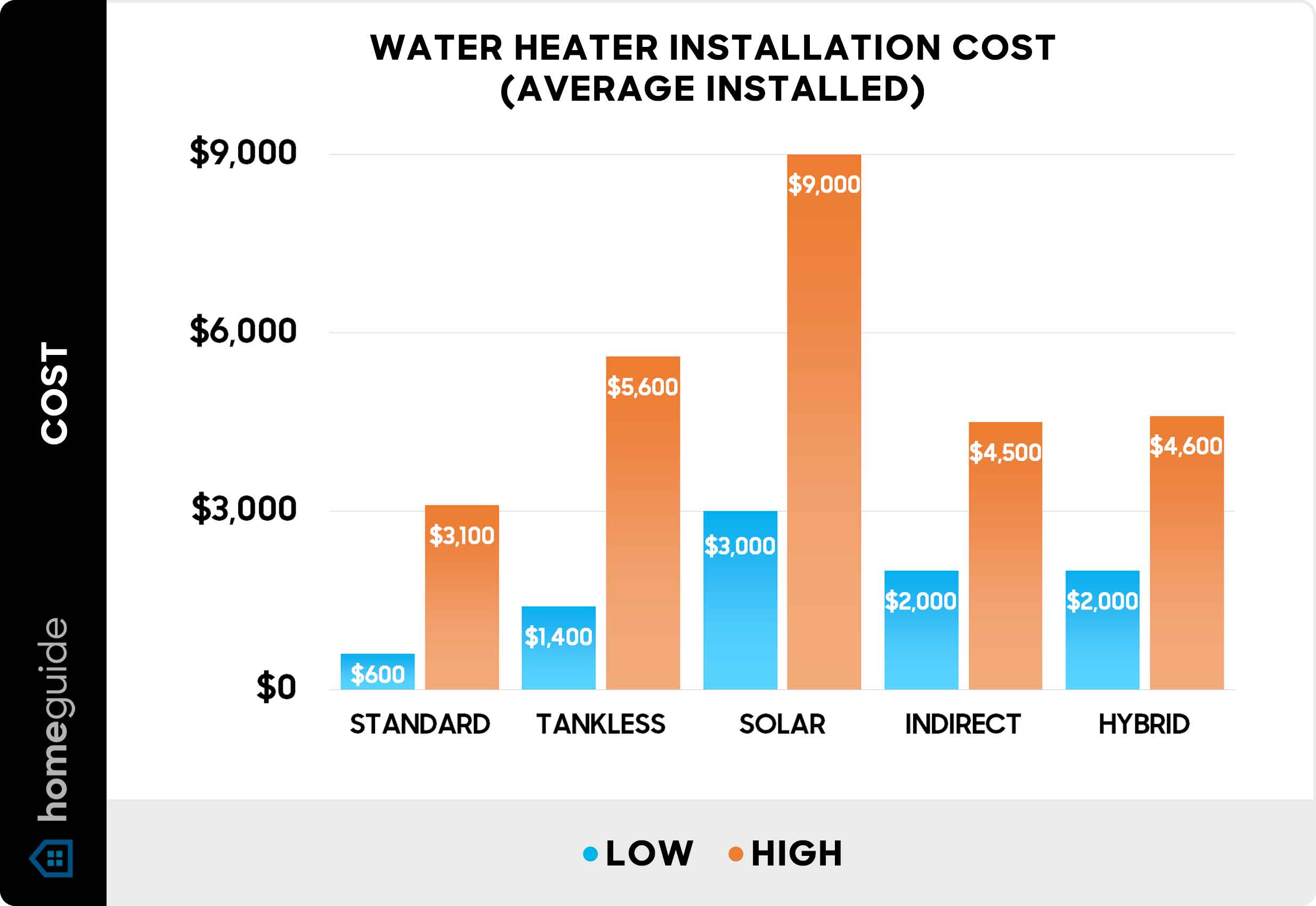
Professional Installation vs. DIY
While some homeowners may be tempted to tackle the installation themselves‚ professional installation is highly recommended. Licensed plumbers and electricians have the expertise to ensure the unit is installed safely and correctly‚ maximizing its efficiency and lifespan. In the middle of this process‚ understanding the intricacies is key to making an informed decision.
Comparative Table: Heat Pump vs. Traditional Water Heaters (Installation Considerations)
| Feature | Heat Pump Water Heater | Traditional Electric Water Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Ventilation Needs | Requires significant airflow and minimum room size. | Minimal ventilation requirements. |
| Ambient Temperature Sensitivity | Performance affected by cold temperatures. | Unaffected by ambient temperature. |
| Condensate Drainage | Requires condensate drainage system. | No condensate drainage required. |
| Complexity of Installation | More complex‚ often requiring professional installation. | Relatively straightforward‚ can be DIY in some cases. |
Ultimately‚ understanding and adhering to the heat pump water heater installation requirements is an investment in long-term energy savings and a sustainable future. By carefully considering the factors outlined above and seeking professional guidance when needed‚ you can ensure a successful installation and reap the full benefits of this energy-efficient technology.
Choosing the right professional is paramount‚ but even then‚ being an informed consumer is crucial. Don’t hesitate to ask potential installers about their experience with heat pump water heaters specifically. Inquire about their understanding of ventilation requirements‚ electrical codes‚ and condensate drainage solutions. A reputable installer should be able to clearly explain the entire process and answer all your questions thoroughly.
TROUBLESHOOTING COMMON INSTALLATION ISSUES
Even with professional installation‚ unforeseen challenges can arise; Being aware of potential issues can help you proactively address them and minimize downtime.
INSUFFICIENT AIRFLOW
One of the most common problems is inadequate airflow. If the unit isn’t drawing enough air‚ it will struggle to heat water efficiently‚ leading to higher energy bills and potentially damaging the compressor. Signs of insufficient airflow include:
– Reduced Hot Water Output: The water may not reach the desired temperature.
– Increased Energy Consumption: The unit runs longer to heat the water.
– Error Codes: Some units display error codes indicating airflow problems.
To address this‚ ensure the area around the unit is clear of obstructions and that ventilation openings are not blocked. You may need to increase the ventilation by adding vents or relocating the unit to a more open space.
CONDENSATE DRAINAGE PROBLEMS
Improper condensate drainage can lead to water damage and mold growth. Ensure the drain line is properly sloped and that there are no kinks or obstructions. Regularly inspect the drain line for clogs and clear them as needed. Consider installing a condensate pump if gravity drainage is not feasible.
ELECTRICAL ISSUES
Electrical problems can range from blown fuses to faulty wiring. If you suspect an electrical issue‚ immediately turn off the power to the unit and contact a qualified electrician. Do not attempt to diagnose or repair electrical problems yourself.
LONG-TERM MAINTENANCE AND CARE
Once your heat pump water heater is installed and running smoothly‚ it’s essential to implement a regular maintenance schedule to ensure its longevity and efficiency.
ANNUAL INSPECTIONS
Schedule an annual inspection with a qualified technician. They can check the unit’s overall performance‚ clean the condenser coils‚ and identify any potential problems before they escalate.
FLUSHING THE TANK
Regularly flush the tank to remove sediment buildup. Sediment can reduce the unit’s efficiency and shorten its lifespan. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the recommended flushing procedure.
AIR FILTER MAINTENANCE
Some heat pump water heaters have air filters that need to be cleaned or replaced regularly. Check the filter monthly and clean or replace it as needed.
MAXIMIZING ENERGY EFFICIENCY
Beyond proper installation and maintenance‚ there are several steps you can take to maximize the energy efficiency of your heat pump water heater.
– Adjust the Thermostat: Lowering the thermostat temperature can significantly reduce energy consumption. A setting of 120°F (49°C) is generally sufficient for most households.
– Insulate Hot Water Pipes: Insulating the hot water pipes can reduce heat loss and improve efficiency.
– Reduce Hot Water Usage: Be mindful of your hot water usage. Take shorter showers‚ wash clothes in cold water whenever possible‚ and fix any leaks promptly.
By following these guidelines‚ you can ensure that your heat pump water heater operates efficiently and reliably for years to come. The initial investment in proper installation and ongoing maintenance will pay off in the form of lower energy bills and a reduced environmental footprint. Don’t underestimate the importance of regular checks‚ and always consult a professional for complex issues. Taking these steps will guarantee you are getting the most out of your new water heater.