Polyvinyl chloride, more commonly known as PVC, has become a ubiquitous material in the construction industry. From plumbing to siding, its versatility and affordability have made it a popular choice for builders and homeowners alike; However, like any material, PVC presents both significant advantages and certain drawbacks that must be carefully considered before incorporating it into a building project. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed decisions about material selection and ensuring the long-term durability and sustainability of structures. Therefore, a thorough exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of **PVC** as a building material is essential.
Advantages of PVC in Construction
PVC boasts a number of compelling advantages that contribute to its widespread adoption:
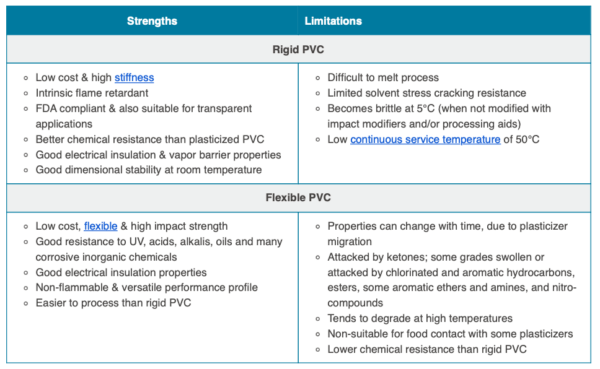
- Durability and Longevity: PVC is resistant to rot, corrosion, and weathering, making it a long-lasting option, especially in harsh environments.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional materials like wood, metal, or concrete, PVC is generally more affordable, reducing overall construction costs.
- Low Maintenance: PVC requires minimal upkeep. It doesn’t need painting, staining, or sealing and is easily cleaned with soap and water.
- Versatility: PVC can be molded into a wide variety of shapes and sizes, allowing for flexible design options.
- Recyclability: While often debated, PVC can be recycled, contributing to sustainable building practices, though recycling infrastructure varies greatly.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC exhibits excellent resistance to many chemicals, making it suitable for use in applications where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern.
- Lightweight: Compared to alternatives like steel or concrete, PVC is lightweight, which simplifies transportation and installation. This, in turn, can reduce labor costs and accelerate construction timelines.
Disadvantages of PVC in Construction
Despite its numerous advantages, PVC also presents certain disadvantages that warrant careful consideration:
- Environmental Concerns: The production of PVC can release harmful chemicals, and its disposal can be problematic due to the potential for dioxin release during incineration.
- Limited Temperature Resistance: PVC can soften or deform at high temperatures, limiting its use in certain applications.
- Aesthetics: While PVC can be manufactured in different colors, its aesthetic appeal may not be as desirable as natural materials like wood or stone for some applications.
- Potential for Leaching: Some studies suggest that PVC can leach chemicals into the environment, particularly in water pipes, although this is more of a concern with older formulations.
- Fire Resistance: PVC is not inherently fire-resistant and can release toxic fumes when burned. Fire-retardant additives can be used, but these can add to the cost and environmental impact.
Comparative Table: PVC vs. Wood
| Feature | PVC | Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly Durable | Susceptible to Rot and Insects |
| Maintenance | Low Maintenance | Requires Regular Painting/Sealing |
| Cost | Generally Lower | Can be Higher Depending on Type |
| Environmental Impact | Potential for Harmful Emissions | Renewable Resource (if sustainably harvested) |
Specific Applications and Considerations
The suitability of PVC as a building material depends heavily on the specific application. For example, PVC pipes are widely used for plumbing due to their cost-effectiveness and resistance to corrosion. However, PVC siding may not be the best choice in areas prone to extreme heat or where a more natural aesthetic is desired. Careful consideration must be given to the environmental impact of **PVC**, including its production, disposal, and potential for leaching.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF PVC AS A BUILDING MATERIAL
Polyvinyl chloride, more commonly known as PVC, has become a ubiquitous material in the construction industry. From plumbing to siding, its versatility and affordability have made it a popular choice for builders and homeowners alike. However, like any material, PVC presents both significant advantages and certain drawbacks that must be carefully considered before incorporating it into a building project. Understanding these nuances is crucial for making informed decisions about material selection and ensuring the long-term durability and sustainability of structures. Therefore, a thorough exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of PVC as a building material is essential.
ADVANTAGES OF PVC IN CONSTRUCTION
PVC boasts a number of compelling advantages that contribute to its widespread adoption:
– Durability and Longevity: PVC is resistant to rot, corrosion, and weathering, making it a long-lasting option, especially in harsh environments.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional materials like wood, metal, or concrete, PVC is generally more affordable, reducing overall construction costs.
– Low Maintenance: PVC requires minimal upkeep. It doesn’t need painting, staining, or sealing and is easily cleaned with soap and water.
– Versatility: PVC can be molded into a wide variety of shapes and sizes, allowing for flexible design options.
– Recyclability: While often debated, PVC can be recycled, contributing to sustainable building practices, though recycling infrastructure varies greatly.
– Chemical Resistance: PVC exhibits excellent resistance to many chemicals, making it suitable for use in applications where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern.
– Lightweight: Compared to alternatives like steel or concrete, PVC is lightweight, which simplifies transportation and installation. This, in turn, can reduce labor costs and accelerate construction timelines.
DISADVANTAGES OF PVC IN CONSTRUCTION
Despite its numerous advantages, PVC also presents certain disadvantages that warrant careful consideration:
– Environmental Concerns: The production of PVC can release harmful chemicals, and its disposal can be problematic due to the potential for dioxin release during incineration.
– Limited Temperature Resistance: PVC can soften or deform at high temperatures, limiting its use in certain applications.
– Aesthetics: While PVC can be manufactured in different colors, its aesthetic appeal may not be as desirable as natural materials like wood or stone for some applications;
– Potential for Leaching: Some studies suggest that PVC can leach chemicals into the environment, particularly in water pipes, although this is more of a concern with older formulations.
– Fire Resistance: PVC is not inherently fire-resistant and can release toxic fumes when burned. Fire-retardant additives can be used, but these can add to the cost and environmental impact;
COMPARATIVE TABLE: PVC VS. WOOD
Feature
PVC
Wood
Emerging Bio-Plastic Alternatives
Durability
Highly Durable
Susceptible to Rot and Insects
Variable, depends on composition
Maintenance
Low Maintenance
Requires Regular Painting/Sealing
Generally Low
Cost
Generally Lower
Can be Higher Depending on Type
Potentially Higher (but decreasing)
Environmental Impact
Potential for Harmful Emissions
Renewable Resource (if sustainably harvested)
Significantly Lower (often biodegradable)
SPECIFIC APPLICATIONS AND CONSIDERATIONS
The suitability of PVC as a building material depends heavily on the specific application. For example, PVC pipes are widely used for plumbing due to their cost-effectiveness and resistance to corrosion. However, PVC siding may not be the best choice in areas prone to extreme heat or where a more natural aesthetic is desired. Careful consideration must be given to the environmental impact of PVC, including its production, disposal, and potential for leaching.
In conclusion, while PVC offers significant advantages in terms of cost, durability, and ease of maintenance, its environmental impact and potential limitations in certain applications must be carefully weighed. As the first sentence stated, understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making responsible and informed decisions in the construction process, ensuring the long-term sustainability and performance of the built environment.
BEYOND THE BINARY: A GLIMPSE INTO THE FUTURE OF BUILDING MATERIALS
But what if the choice wasn’t simply PVC *or* something else? What if innovation could bridge the gap between affordability and sustainability? Imagine walls that breathe, foundations that heal themselves, and roofs that generate power. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the burgeoning reality of bio-based building materials. Think mycelium bricks, grown from mushroom roots and agricultural waste, offering incredible insulation and fire resistance. Or hempcrete, a concrete alternative made from hemp fibers and lime, sequestering carbon as it solidifies. These materials, still in their relative infancy, promise to revolutionize the construction landscape, offering compelling alternatives to the established dominance of materials like PVC. They challenge us to reconsider our relationship with the built environment, moving towards systems that are not just functional, but regenerative.
THE ALGAE REVOLUTION: BUILDING WITH LIVING SYSTEMS
Forget static structures; imagine buildings that are actively alive. Algae-based facades, for example, can not only provide insulation and shade but also generate biofuel and purify wastewater. These “living walls” are essentially miniature ecosystems, constantly adapting to their environment and providing a range of benefits beyond simple shelter. While challenges remain in scaling up these technologies and ensuring their long-term viability, the potential is undeniable. We are entering an era where buildings are not just inert objects but active participants in the ecological cycle. These innovations invite us to dream of cities that are not just concrete jungles, but thriving, self-sustaining ecosystems, harmonizing technology and nature in unexpected and beautiful ways. The future of building isn’t just about what we build *with*, but *how* we build, and *why*.
A PARADIGM SHIFT: FROM CONSUMPTION TO CREATION
Ultimately, the debate surrounding PVC and other traditional building materials points to a deeper need for a paradigm shift in our approach to construction. We need to move away from a linear model of consumption and waste towards a circular economy, where materials are constantly recycled and reused. This requires a fundamental rethinking of design, manufacturing, and demolition processes. It means prioritizing durability and adaptability over short-term cost savings. And it demands a commitment to innovation and collaboration, bringing together scientists, engineers, architects, and policymakers to create a more sustainable and resilient built environment. The future of construction is not just about finding better materials; it’s about creating a better world.