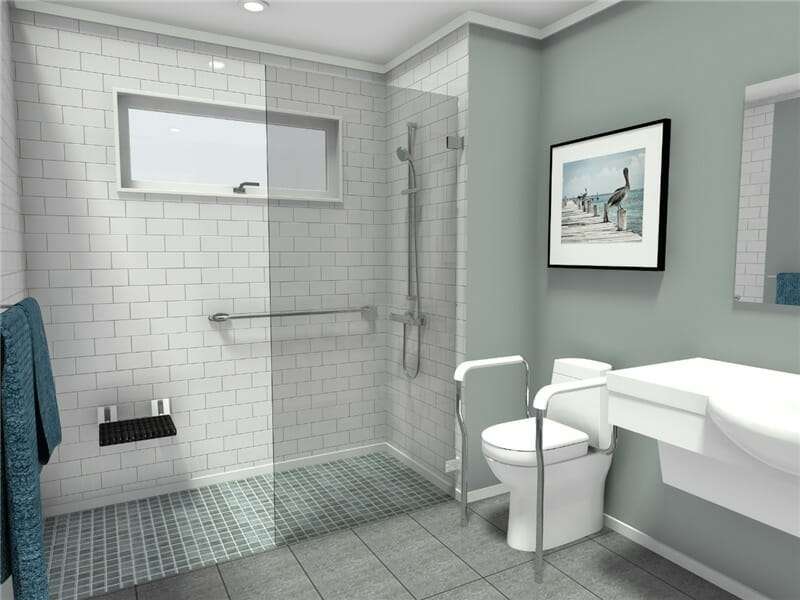
Creating a truly accessible bathroom requires careful consideration of numerous factors beyond simply meeting minimum code requirements. A well-designed wheelchair accessible bathroom offers independence and dignity to users, allowing them to perform daily hygiene tasks with ease and comfort. The goal is to create a space that is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing, avoiding the institutional feel that can sometimes be associated with accessible design. Effective wheelchair accessible bathroom design balances practicality with a welcoming atmosphere, enhancing the overall quality of life for the individual using the space.
Key Considerations for Accessible Bathroom Design
When planning a wheelchair accessible bathroom, several key areas need particular attention. These include:
- Space and Layout: Ample maneuvering space is critical. A turning radius of at least 60 inches (1525 mm) is generally recommended for wheelchairs. Clear floor space should be provided at fixtures like the sink, toilet, and shower.
- Fixtures and Fittings: Selecting the right fixtures is crucial. Consider adjustable-height sinks, grab bars strategically placed around the toilet and shower, and lever-handled faucets for ease of use.
- Doorways and Access: Doorways should be at least 32 inches (815 mm) wide to accommodate wheelchairs. Consider using swing-clear hinges to maximize the opening.
Specific Fixture Adaptations
Let’s delve deeper into the specific adaptations required for each fixture:
Toilet Accessibility
- Height: Toilets should be installed at a height that allows for easy transfer from a wheelchair. Typically, this is between 17 and 19 inches (430-485 mm) to the top of the seat.
- Grab Bars: Securely mounted grab bars are essential for stability and support. They should be positioned on the side and behind the toilet.
- Space: Adequate clear space beside the toilet is necessary for wheelchair positioning.
Sink Accessibility
- Height: Sinks should be mounted at a height that allows wheelchair users to easily reach the faucet and basin. Aim for a maximum rim height of 34 inches (865 mm).
- Knee Clearance: Provide adequate knee clearance beneath the sink, typically at least 27 inches (685 mm) high, 30 inches (760 mm) wide, and 19 inches (485 mm) deep.
- Faucet: Lever-handled or touchless faucets are easier to operate for individuals with limited dexterity.
Shower Accessibility
Showers present unique challenges and require careful planning. Options include roll-in showers with no curb, or showers with low thresholds. A fold-down seat is highly recommended.
The right wheelchair accessible bathroom design can significantly improve the independence and comfort of the user. Pay close attention to all the details.
Comparative Table: Traditional vs. Accessible Bathroom Features
| Feature | Traditional Bathroom | Wheelchair Accessible Bathroom |
|---|---|---|
| Toilet Height | Standard Height (15-17 inches) | Comfort Height (17-19 inches) |
| Sink Height | Standard Height (31-36 inches) | Adjustable or Lowered Height (Max 34 inches) |
| Grab Bars | Usually Absent | Required at Toilet and Shower |
| Doorway Width | Typically 24-30 inches | Minimum 32 inches |
| Turning Radius | Limited Space | Minimum 60 inches |
Ultimately, a successful wheelchair accessible bathroom design is one that prioritizes the user’s needs and preferences. By carefully considering all aspects of the design, it is possible to create a bathroom that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing, enhancing the quality of life for individuals with mobility challenges. Remember, thoughtful planning and attention to detail are key to achieving a truly accessible and comfortable bathroom experience.