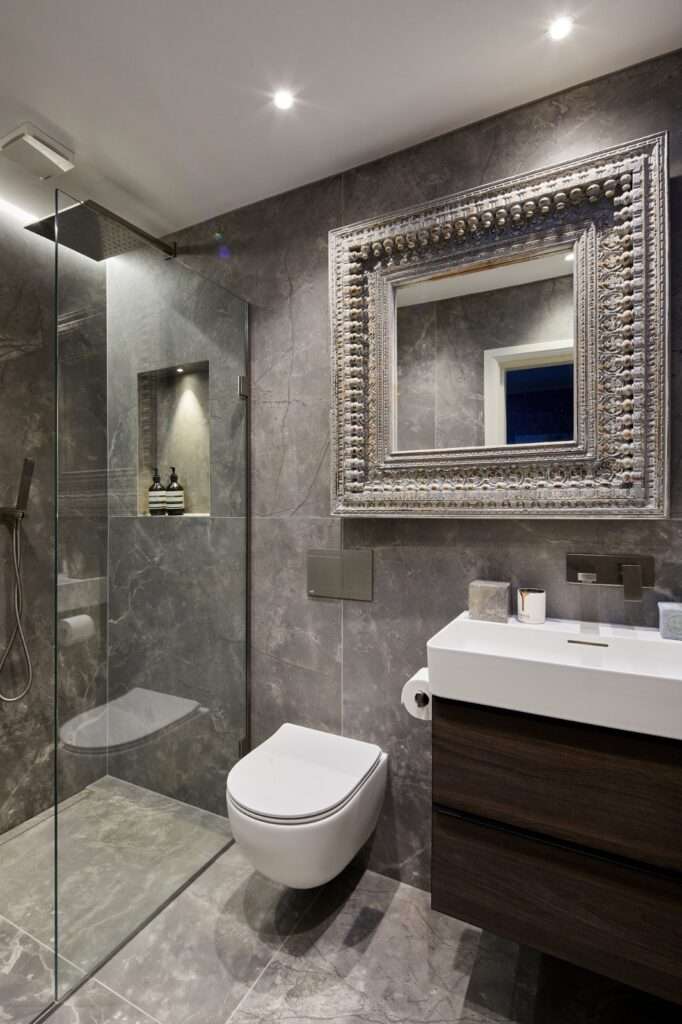
Embarking on a kitchen or bathroom renovation can feel overwhelming, but finding the right professional support can make all the difference. Searching for “kitchen and bathroom designers near me” is the first step towards transforming your vision into a reality. The best designers will not only bring creative ideas to the table, but also possess the technical expertise to manage the project efficiently, ensuring a smooth and stress-free experience. Consider factors like their portfolio, client testimonials, and communication style to find a designer who aligns with your specific needs and preferences. Finding the right kitchen and bathroom designers near me is about creating a functional and beautiful space.
Why Hire a Kitchen and Bathroom Designer?
While tackling a DIY renovation might seem tempting, engaging a professional designer offers numerous advantages:
- Expertise and Experience: Designers possess in-depth knowledge of spatial planning, material selection, and current design trends.
- Project Management: They can oversee the entire project, from initial concept to final installation, coordinating with contractors and ensuring timelines are met.
- Cost Savings: Although there is an initial investment, designers can help you avoid costly mistakes and optimize your budget by sourcing materials and fixtures effectively;
- Increased Home Value: A well-designed kitchen or bathroom can significantly enhance the value and appeal of your home.
Finding the Right Fit: Key Considerations
With so many options available, how do you narrow down your search for the perfect designer? Here are some important factors to consider:
- Portfolio Review: Examine their previous work to assess their design style and aesthetic. Does it align with your vision?
- Client Testimonials: Read reviews and testimonials to gauge their professionalism, communication skills, and overall client satisfaction.
- Licensing and Insurance: Ensure they are properly licensed and insured to protect yourself from liability.
- Communication Style: Choose a designer who is responsive, attentive, and clearly communicates throughout the project.
- Budget and Timeline: Discuss your budget and desired timeline upfront to ensure they are realistic and manageable.
Questions to Ask Potential Designers
Before hiring a designer, be sure to ask these crucial questions:
- What is your design process?
- What is your experience with projects similar to mine?
- How do you handle unexpected challenges or delays?
- What are your fees and payment terms?
- Can you provide references from previous clients?
The Design Process: What to Expect
The design process typically involves several stages:
- Initial Consultation: Discuss your needs, preferences, and budget.
- Concept Development: The designer will create preliminary designs and layouts based on your input.
- Design Refinement: You’ll work together to refine the design, selecting materials, fixtures, and finishes.
- Construction Documentation: The designer will create detailed drawings and specifications for the contractors.
- Project Management: The designer will oversee the construction process, ensuring the design is executed accurately.
Investing in professional design services is a worthwhile investment for any kitchen or bathroom renovation project. By carefully researching and selecting the right designer, you can transform your space into a beautiful and functional oasis.
Ultimately, finding the right “kitchen and bathroom designers near me” is about finding someone who understands your vision, possesses the expertise to bring it to life, and provides a seamless and enjoyable renovation experience.