Creating a bathroom that is both stylish and easy to maintain is a dream for many homeowners. Nobody wants to spend hours scrubbing tiles and battling mildew. The key lies in smart design choices that prioritize functionality and minimize areas where dirt and grime can accumulate. Implementing these easy to clean bathroom design ideas will not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of your space but also significantly reduce your cleaning workload. Let’s explore some innovative solutions that will transform your bathroom into a haven of cleanliness and relaxation.
Choosing the Right Materials
Selecting the right materials is crucial for an easy-to-clean bathroom. Certain materials are naturally more resistant to stains, mold, and mildew, making them ideal choices for this high-moisture environment.
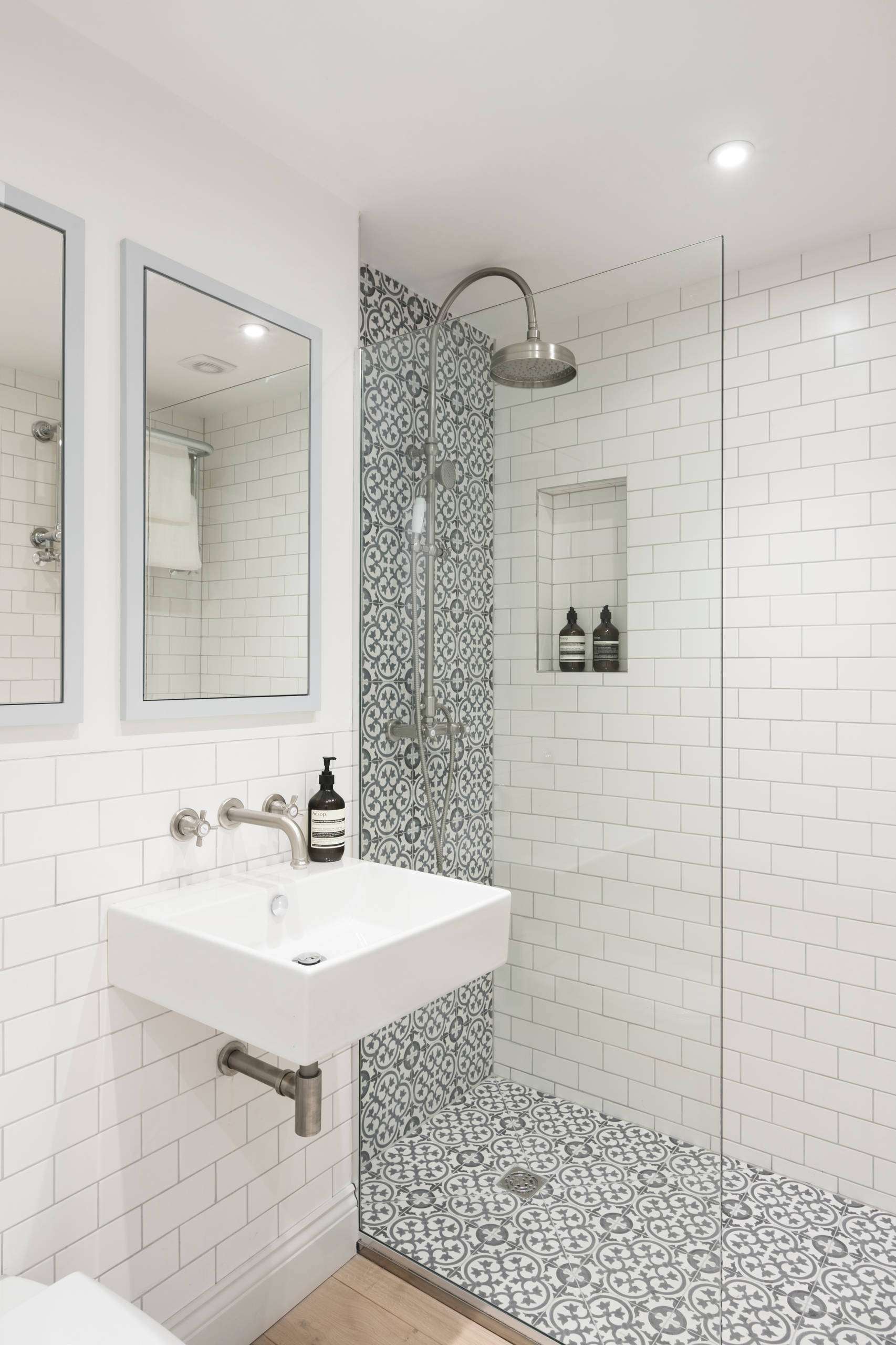
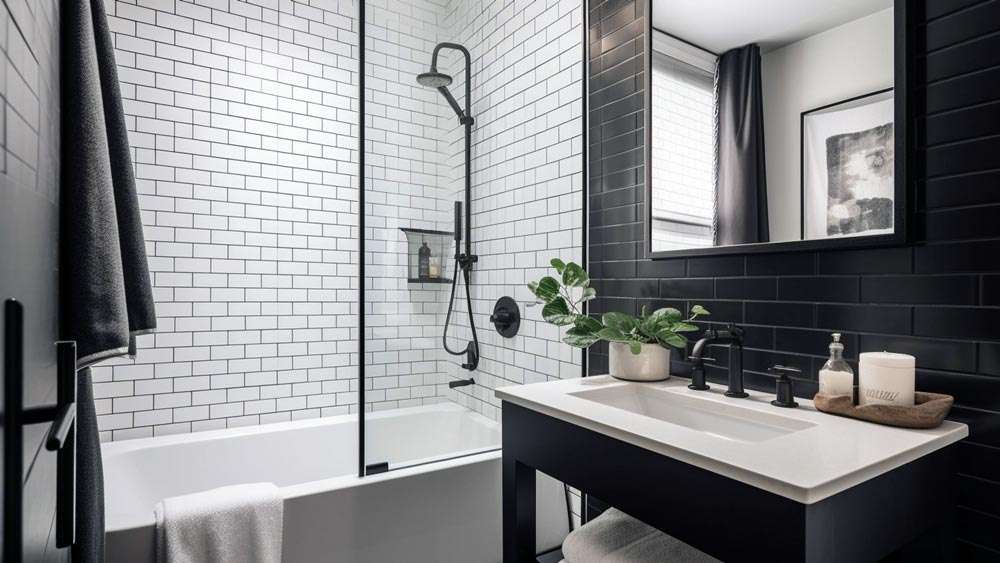
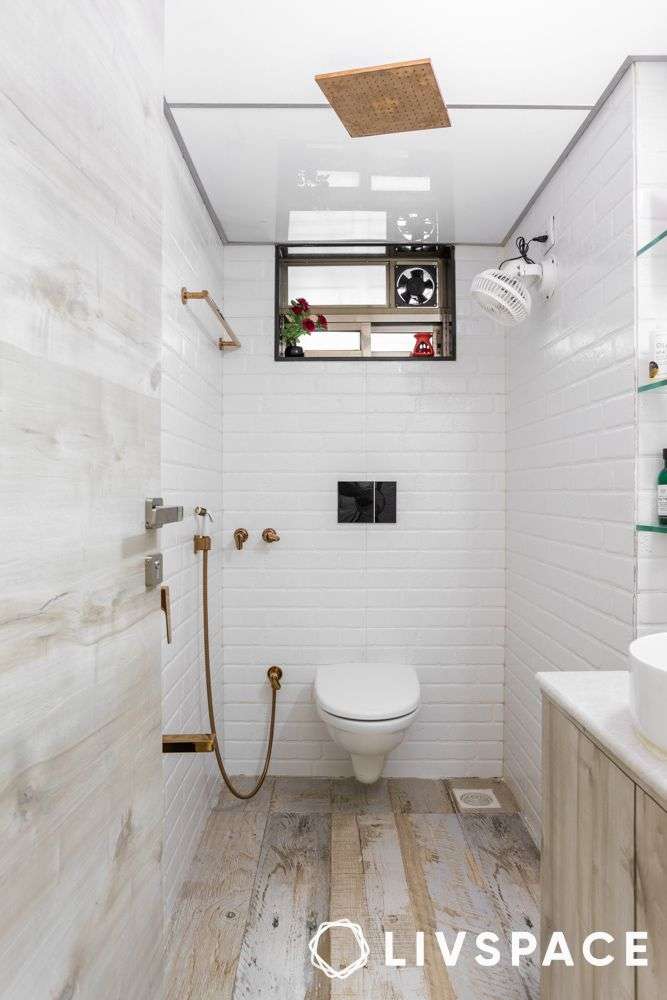
- Large Format Tiles: Fewer grout lines mean less area for dirt and grime to collect. Opt for rectified tiles for even tighter grout joints.
- Solid Surface Countertops: Materials like quartz and solid acrylic are non-porous and resist staining and bacteria growth.
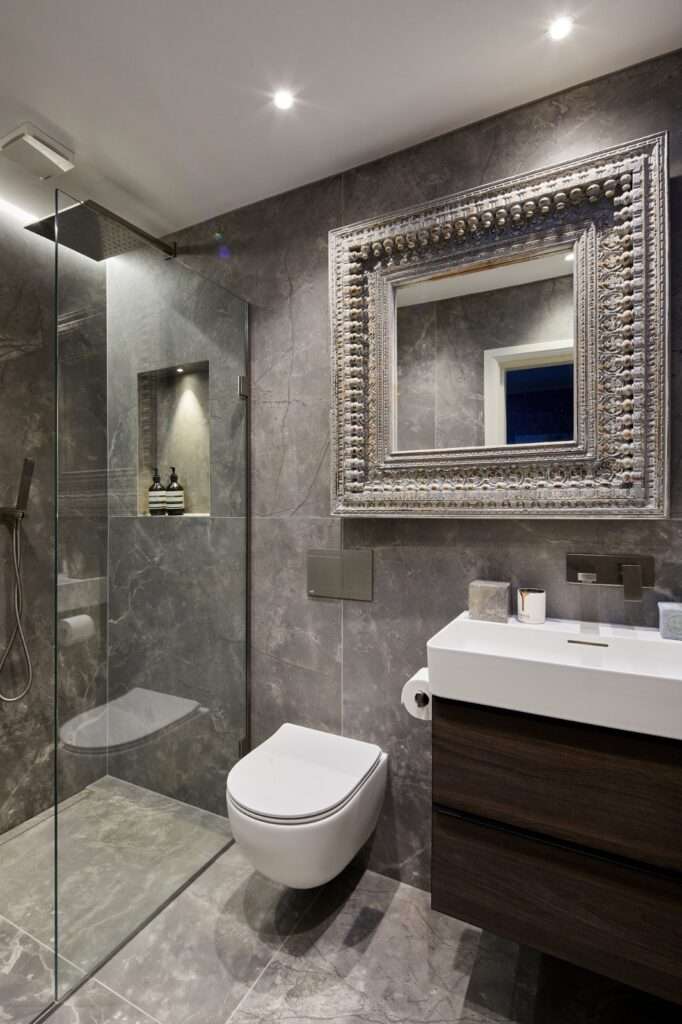
- Glass Shower Doors: Choose glass with a protective coating that repels water and soap scum.
- Epoxy Grout: Unlike traditional grout, epoxy grout is non-porous and resistant to staining and mildew.
Smart Fixture Choices
The fixtures you choose can also significantly impact the ease of cleaning. Consider the following options:
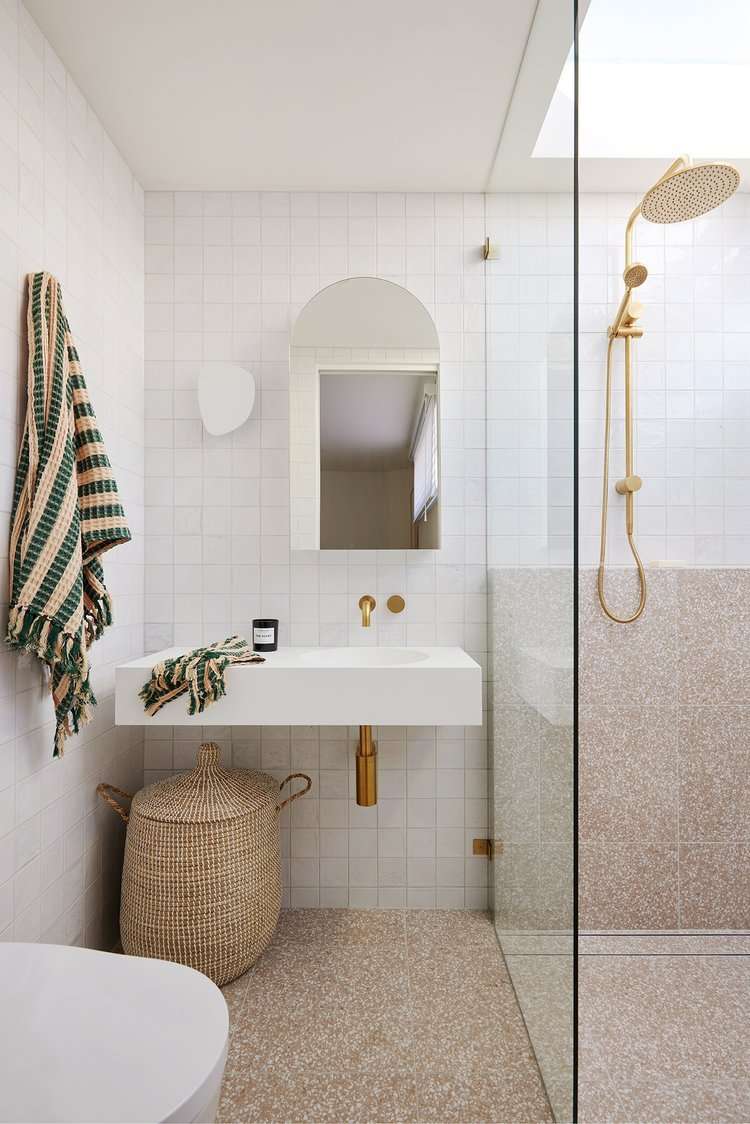
- Wall-Mounted Toilets and Vanities: These create more open space on the floor, making it easier to sweep and mop.
- One-Piece Toilets: Fewer crevices mean less places for dirt to hide.
- Touchless Faucets: Reduce the spread of germs and minimize water spots.
- Shower Niches: Built-in shower niches provide convenient storage for toiletries and eliminate the need for clutter-prone shelves.
Ventilation is Key
Proper ventilation is essential for preventing moisture buildup and mold growth in the bathroom. A powerful exhaust fan that is properly sized for the room can help to quickly remove excess moisture after showers and baths. Make sure the fan is used every time you shower or bathe, and leave it running for at least 20 minutes afterward. This simple habit can drastically reduce the amount of cleaning required.
Comparative Table: Cleaning Material Comparison
| Material | Pros | Cons | Cleaning Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz Countertops | Durable, non-porous, stain-resistant | Can be expensive | Easy |
| Granite Countertops | Natural stone, heat-resistant | Porous, requires sealing | Medium |
| Laminate Countertops | Affordable, wide variety of colors and patterns | Susceptible to scratches and water damage | Medium |
| Large Format Tiles | Fewer grout lines, modern look | Can be difficult to install | Easy |
Streamlining Storage Solutions
Clutter is the enemy of a clean bathroom. Implementing smart storage solutions can help to keep surfaces clear and make cleaning much easier.
Ideas for Streamlining Storage:
- Vanity with Drawers and Shelves: Provides ample storage for toiletries and personal care items.
- Medicine Cabinet: Keeps everyday essentials organized and within easy reach.
- Over-the-Toilet Storage: Utilizes vertical space for towels, toiletries, and other necessities.
- Baskets and Bins: Perfect for corralling smaller items and keeping them organized.
Finally, remember that achieving an easy to clean bathroom design doesn’t require a complete overhaul. Even small changes, like switching to microfiber cloths for cleaning or using a squeegee after each shower, can make a big difference. Embracing these design and maintenance tips will ensure your bathroom remains a clean, comfortable, and inviting space for years to come.
Implementing these meticulous considerations during the design phase of a bathroom renovation or new construction project will yield a space that minimizes maintenance demands while retaining aesthetic appeal. Furthermore, the consistent application of preventative measures, such as prompt spill cleanup and regular ventilation, will significantly contribute to the long-term preservation of the bathroom’s cleanliness and hygiene.
ADVANCED CLEANING TECHNIQUES AND PRODUCT SELECTION
Beyond the initial design and material choices, the selection of appropriate cleaning products and the adoption of refined cleaning techniques are paramount for maintaining an easily cleaned bathroom environment. The efficacy of cleaning protocols is directly contingent upon the synergistic relationship between the cleaning agent employed and the surface being treated.
– pH-Neutral Cleaners: These are generally recommended for daily maintenance of most bathroom surfaces, as they are less likely to cause damage or discoloration.
– Specialized Tile and Grout Cleaners: For periodic deep cleaning, specifically formulated tile and grout cleaners can effectively remove stubborn stains and mildew.
– Glass Cleaners with Anti-Spotting Agents: The utilization of these products on shower doors and mirrors will significantly reduce water spot accumulation and maintain clarity.
– Microfiber Cleaning Cloths: These cloths are highly effective at trapping dirt and grime without scratching surfaces.
THE ROLE OF AUTOMATION AND TECHNOLOGY
The integration of automated systems and technological advancements can further streamline bathroom cleaning processes and minimize manual intervention. These innovations offer both convenience and enhanced hygiene.
– Automatic Toilet Bowl Cleaners: These devices dispense a measured amount of cleaning solution with each flush, inhibiting the buildup of stains and bacteria.
– Self-Cleaning Toilets: Some advanced toilet models feature built-in self-cleaning cycles that utilize UV light or other disinfection methods to sanitize the bowl.
– Smart Shower Systems: These systems can be programmed to automatically flush the pipes after each use, preventing stagnation and the growth of bacteria.
– Robotic Floor Cleaners: Compact robotic vacuums can be employed to regularly clean bathroom floors, removing dust and debris.
ADDRESSING COMMON BATHROOM CLEANING CHALLENGES
Despite diligent cleaning efforts, certain bathroom areas often present persistent challenges. Addressing these issues requires targeted strategies and the application of specialized techniques.
SPECIFIC CLEANING CHALLENGES AND SOLUTIONS:
– Soap Scum Buildup: Apply a solution of warm water and white vinegar to dissolve soap scum. For stubborn deposits, use a non-abrasive scrub brush.
– Mold and Mildew Growth: Treat affected areas with a bleach solution (always dilute bleach with water and ensure adequate ventilation). Alternatively, use a commercially available mold and mildew remover.
– Hard Water Stains: Mineral deposits from hard water can be removed with a solution of lemon juice or vinegar. For severe staining, consider using a commercial hard water stain remover.
– Clogged Drains: Regularly flush drains with hot water to prevent blockages. For clogs, use a drain snake or a chemical drain cleaner (exercise caution when using chemical drain cleaners and follow the manufacturer’s instructions).
Maintaining an environment that epitomizes both cleanliness and aesthetic appeal necessitates a holistic approach encompassing judicious material selection, proactive preventative measures, and the strategic application of advanced cleaning techniques. By meticulously addressing each facet of bathroom design and maintenance, it is feasible to cultivate a sanctuary of hygiene and tranquility, thereby diminishing the demands of routine cleaning and maximizing the enjoyment of the space. The implementation of these easy to clean bathroom design ideas will contribute to a more manageable and hygienic home environment.