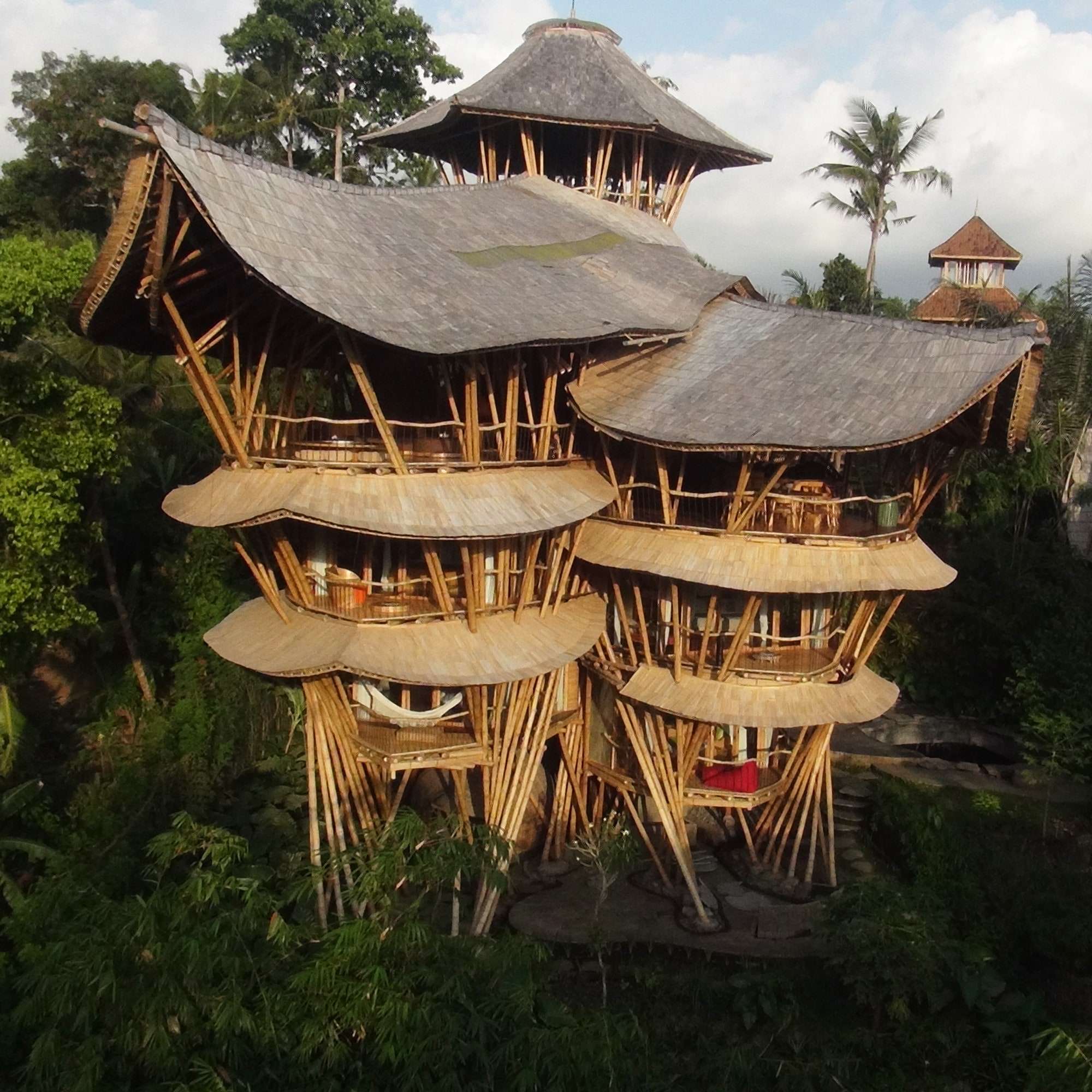
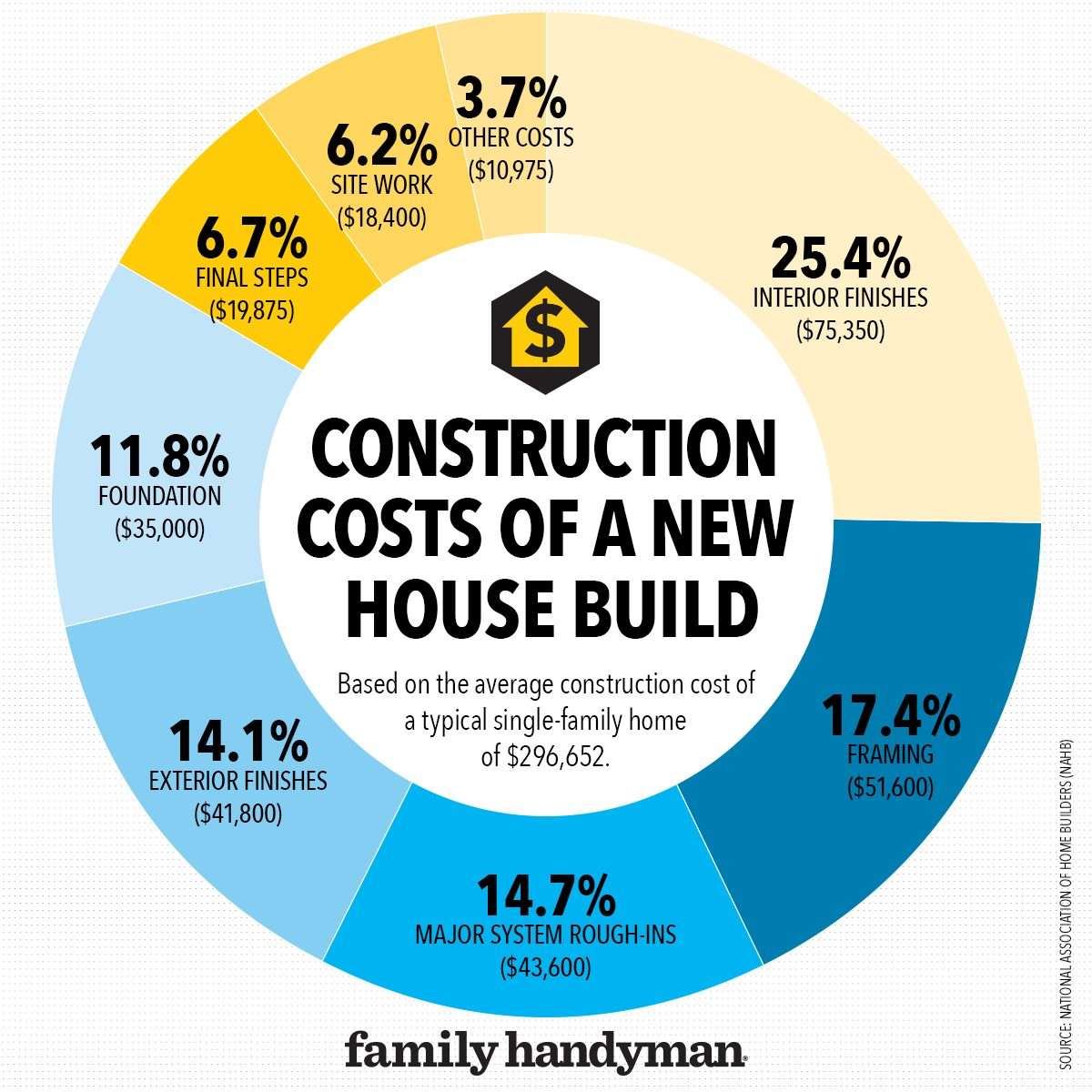
Bamboo, often overlooked in modern construction, presents a compelling alternative to traditional building materials like concrete and steel. Its rapid growth rate makes it a remarkably sustainable resource, contributing significantly to reducing deforestation and promoting ecological balance. The tensile strength of bamboo rivals that of steel, offering exceptional structural integrity for a variety of construction projects. Furthermore, the inherent flexibility of bamboo allows for innovative architectural designs, pushing the boundaries of conventional building aesthetics. The advantages of using bamboo as a building material are becoming increasingly clear as we strive for a more environmentally conscious future.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
- Rapid Growth and Renewability: Bamboo is one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth, reaching maturity in just a few years compared to decades for hardwood trees. This rapid regeneration makes it a highly renewable resource.
- Carbon Sequestration: Bamboo absorbs significant amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate climate change. Harvesting bamboo doesn’t kill the plant, allowing it to continue sequestering carbon.
- Soil Erosion Control: Bamboo’s extensive root system helps to stabilize soil and prevent erosion, especially on slopes and in areas prone to landslides.
- Reduced Deforestation: By using bamboo as a building material, we can reduce the demand for timber, helping to protect forests and biodiversity.
Structural Properties and Durability
Beyond its environmental benefits, bamboo boasts impressive structural characteristics. Its high tensile strength, comparable to steel, makes it suitable for load-bearing applications. Properly treated bamboo is also resistant to pests and decay, ensuring long-lasting structures.
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Bamboo possesses an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it a lightweight yet robust building material. This translates to reduced transportation costs and easier handling on construction sites.
Natural Flexibility and Earthquake Resistance
The inherent flexibility of bamboo allows it to withstand seismic forces, making it a resilient building material in earthquake-prone regions. Its ability to bend and sway without breaking significantly reduces the risk of structural collapse.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
In many regions, bamboo is a readily available and relatively inexpensive building material. This makes it a particularly attractive option for affordable housing projects and communities with limited resources.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Versatility
Bamboo’s natural beauty and unique texture add a distinctive aesthetic appeal to buildings. Its flexibility allows for creative and innovative architectural designs, pushing the boundaries of traditional construction.
The advantages of using bamboo as a building material are undeniable, offering a sustainable, strong, and aesthetically pleasing alternative to conventional options. As awareness of its benefits grows, we can expect to see bamboo increasingly incorporated into construction projects around the world, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient built environment. While there are challenges to overcome, such as ensuring proper treatment and standardization, the potential of bamboo as a building material is immense. Let us embrace this natural resource and unlock its full potential to create a better future for generations to come.
CHALLENGES AND CONSIDERATIONS
While the benefits of bamboo are substantial, some challenges need to be addressed to ensure its widespread adoption as a mainstream building material. These challenges include:
– Durability and Treatment: Bamboo is susceptible to insect infestation and decay if not properly treated. Effective and environmentally friendly preservation methods are crucial for extending its lifespan.
– Standardization and Quality Control: Lack of standardized grading and quality control processes can hinder confidence in bamboo as a reliable building material. Developing and implementing industry-wide standards is essential.
– Building Codes and Regulations: Many building codes do not yet fully recognize or address the use of bamboo in construction. Updating regulations to incorporate bamboo as a recognized and approved material is necessary.
– Public Perception: Overcoming misconceptions about the strength and durability of bamboo is important. Education and demonstration projects can help to change perceptions and build confidence.
APPLICATIONS OF BAMBOO IN CONSTRUCTION
Bamboo can be utilized in a wide range of construction applications, from simple shelters to complex structures. Some common uses include:
– Housing: Bamboo is well-suited for building affordable and sustainable homes, particularly in developing countries.
– Bridges: Bamboo can be used to construct pedestrian and vehicular bridges, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to concrete and steel.
– Scaffolding: In many parts of Asia, bamboo is traditionally used for scaffolding due to its strength, flexibility, and lightweight properties.
– Roofing: Bamboo culms can be split and woven into roofing panels, providing a durable and weather-resistant covering.
– Flooring: Bamboo flooring is a popular choice for its durability, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal.
– Furniture: Bamboo is a versatile material for creating furniture, offering a sustainable alternative to timber.
THE FUTURE OF BAMBOO IN CONSTRUCTION
As the world increasingly focuses on sustainable development, the use of bamboo as a building material is poised for significant growth. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving bamboo treatment methods, developing innovative construction techniques, and promoting the standardization of bamboo products. The increasing awareness of the environmental and economic benefits of bamboo will undoubtedly drive its adoption in construction projects worldwide. With continued innovation and collaboration, bamboo has the potential to revolutionize the building industry and contribute to a more sustainable future.