The longevity and structural integrity of any building are intrinsically linked to maintaining acceptable moisture content in its constituent materials. Understanding and controlling moisture levels is not merely a matter of preventing unsightly mold growth; it’s about safeguarding the entire building envelope from deterioration‚ decay‚ and potential health hazards. Achieving acceptable moisture content ensures that materials retain their intended strength and insulating properties‚ contributing to a more comfortable and energy-efficient indoor environment. This article delves into the specifics of managing **acceptable moisture content in building materials** to promote a durable and healthy built environment.
Why Moisture Control is Crucial
Excess moisture within building materials can lead to a cascade of problems‚ impacting both the structure and the occupants’ well-being. Here’s a breakdown of the key issues:
- Structural Damage: Wood rot‚ corrosion of metals‚ and degradation of concrete are all potential consequences of prolonged exposure to excessive moisture.
- Mold and Mildew Growth: Damp conditions provide the perfect breeding ground for mold and mildew‚ which can trigger allergic reactions‚ respiratory problems‚ and other health issues.
- Reduced Insulation Efficiency: Wet insulation loses its ability to effectively insulate‚ leading to higher energy bills and a less comfortable indoor climate.
- Compromised Air Quality: Mold and mildew spores‚ as well as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released from damp materials‚ can contaminate indoor air‚ posing health risks to occupants.
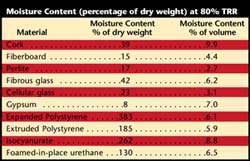
Acceptable Moisture Content Levels for Common Building Materials
The ideal moisture content varies depending on the specific material. Here’s a general guide:
Wood
For most interior applications‚ wood should have a moisture content between 6% and 12%. Exterior wood may tolerate slightly higher levels‚ but should still be carefully monitored to prevent rot.
Concrete
Concrete moisture content is typically measured as relative humidity within the concrete slab. Acceptable levels prior to flooring installation are often specified by the flooring manufacturer‚ but generally should be below 75% RH.
Gypsum Board (Drywall)
Gypsum board should ideally have a moisture content below 1%. Elevated levels can lead to mold growth and structural damage.
Methods for Controlling Moisture
Effective moisture control strategies involve a combination of design‚ construction‚ and maintenance practices:
- Proper Ventilation: Adequate ventilation helps to remove excess moisture from the air.
- Effective Waterproofing: Properly installed and maintained waterproofing systems prevent water from entering the building envelope.
- Vapor Barriers: Vapor barriers help to prevent moisture from diffusing through walls and ceilings.
- Regular Inspections: Routine inspections can identify potential moisture problems before they escalate.
- Prompt Repairs: Addressing leaks and other sources of moisture promptly is essential to prevent damage.
Comparative Table: Moisture Content and Its Impact
| Material | Acceptable Moisture Content | Potential Problems with Excess Moisture |
|---|---|---|
| Wood | 6-12% | Rot‚ decay‚ warping |
| Concrete | Below 75% RH | Mold growth‚ adhesive failure |
| Gypsum Board | Below 1% | Mold growth‚ structural damage |
Furthermore‚ the selection of appropriate building materials tailored to the specific climate and environmental conditions is of paramount importance. Porous materials‚ while offering certain aesthetic and functional advantages‚ may exhibit a greater susceptibility to moisture absorption and retention. Consequently‚ their application in regions characterized by high humidity or frequent precipitation necessitates the implementation of enhanced moisture management strategies. This may encompass the utilization of specialized coatings‚ sealants‚ and drainage systems designed to mitigate the ingress of water and facilitate its subsequent evacuation.
ADVANCED MOISTURE MONITORING TECHNIQUES
Beyond visual inspections‚ sophisticated moisture monitoring technologies provide a more accurate and comprehensive assessment of moisture levels within building materials; These techniques often employ non-destructive methods to minimize disruption and potential damage to the structure;
– Moisture Meters: These handheld devices measure the electrical resistance or capacitance of a material‚ which correlates to its moisture content. Pin-type meters require direct contact‚ while pinless meters utilize electromagnetic fields for non-invasive measurements.
– Infrared Thermography: This technique utilizes infrared cameras to detect temperature variations on surfaces. Evaporative cooling associated with moisture can reveal areas of elevated moisture content that may not be readily apparent.
– Relative Humidity Probes: These probes are inserted into small holes drilled into materials‚ such as concrete‚ to measure the relative humidity within the material itself. This provides a more accurate indication of moisture levels compared to surface measurements.
THE ROLE OF BUILDING CODES AND STANDARDS
Building codes and standards play a crucial role in establishing minimum requirements for moisture control in construction. These regulations often specify acceptable moisture content levels for various building materials‚ as well as guidelines for vapor barrier installation‚ ventilation‚ and waterproofing. Adherence to these codes and standards is essential for ensuring the durability and safety of buildings.
FUTURE TRENDS IN MOISTURE MANAGEMENT
The field of moisture management is constantly evolving‚ with ongoing research and development focused on innovative materials and technologies. Self-healing materials‚ for instance‚ have the potential to automatically repair minor cracks and breaches in building envelopes‚ preventing water intrusion. Smart building systems‚ equipped with sensors and data analytics‚ can continuously monitor moisture levels and automatically adjust ventilation and humidity control systems to maintain optimal conditions. The integration of these advancements promises to further enhance the effectiveness of moisture management strategies and promote the longevity of buildings.
Ultimately‚ achieving and maintaining **acceptable moisture content in building materials** requires a holistic and proactive approach. This encompasses careful material selection‚ meticulous construction practices‚ diligent maintenance‚ and the adoption of advanced monitoring technologies. By prioritizing moisture control‚ we can safeguard the structural integrity of buildings‚ protect the health and well-being of occupants‚ and contribute to a more sustainable built environment.